Gold Milling Production Process Solution for Gold Ore
I. Overview: a classic and highly efficient coarse-grained gold recovery process
The gold milling process is a physical beneficiation method based on the combination of crushing - grinding - re-election - amalgamation, which is specially used to process ores containing coarse-grained exposed natural gold. The core equipment is an electric mill, which grinds the ore through the pressure and shear force of the milling disc to dissociate the gold particles and realize the rapid recovery of gold by using the amalgamated mercury (mercury)'s gold-loving property. The gold milling production process has irreplaceable advantages in specific application scenarios due to its remarkable features of small investment, quick results and simple operation.
Core production process
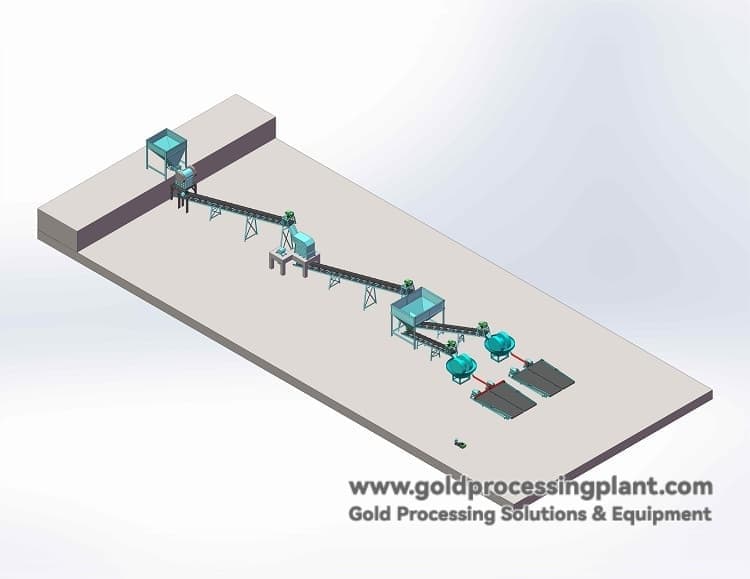
A complete set of gold milling production line mainly contains the following links:
-
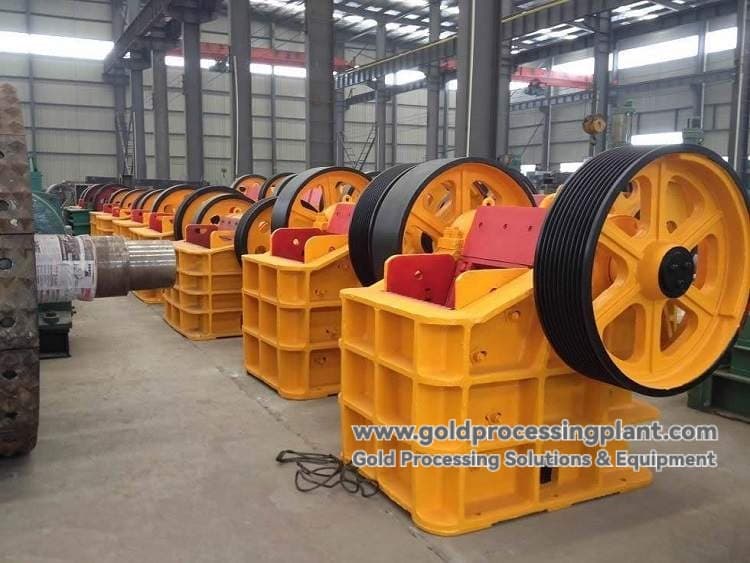
Crushing stage
-
Rough crushing by jaw crusher: crushing the raw ore to medium size.
-
Direct fine crushing by using the drop difference: utilizing the height difference of the terrain, the materials naturally fall into the secondary fine crushing equipment (such as fine jaw crusher or roller crusher), saving energy consumption and equipment.
-
Conveying and Feeding
-
Belt conveyor: conveying the crushed materials to the bin above the mill.
-
Vibrating feeder: located at the bottom of the silo, it can adjust the feeding speed and control the handling capacity to ensure uniform and stable material supply to the mill.
-
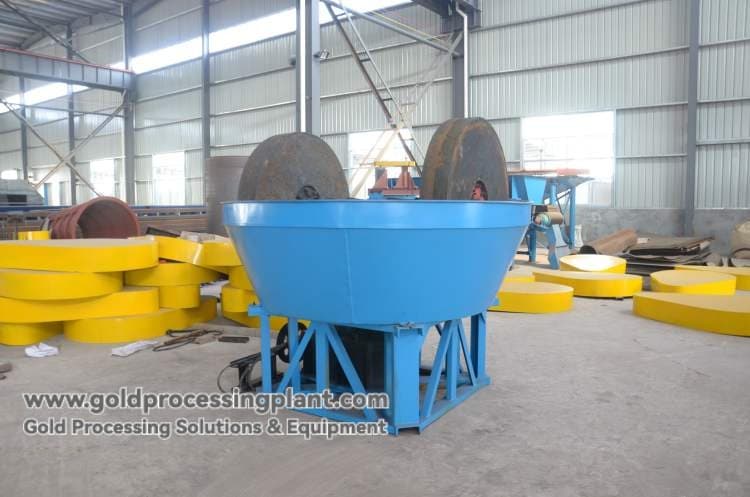
Grinding and sorting (core link)
-
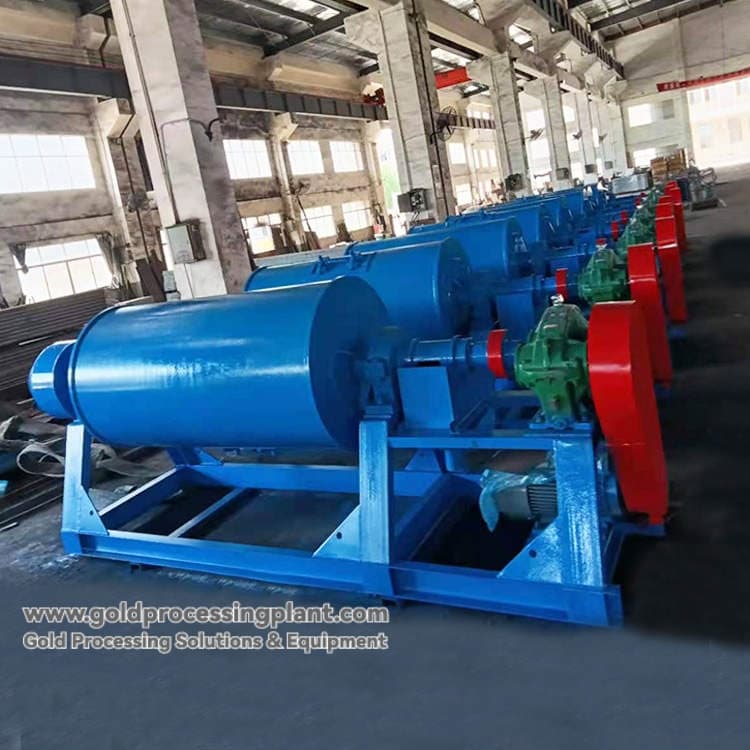
Mills Grinding: Electric mills are the core equipment to realize the full dissociation of gold particles through the gravity grinding and milling of the mills.
-
Mesh sieve: Installed in front of the mill, it is used to control the particle size of the material entering the mill to prevent the equipment from being damaged by too coarse lump ore.
-
Homemade disperser: to make the slurry evenly distributed and improve the efficiency of grinding and sorting.
-
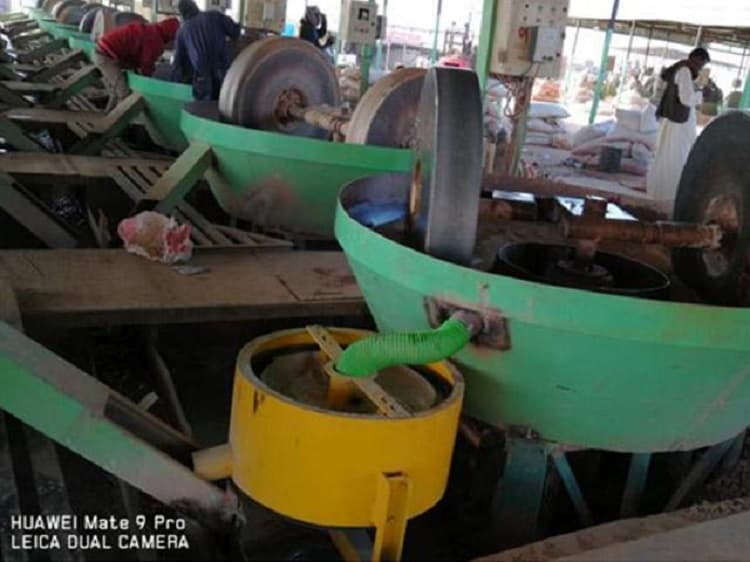
Amalgamation to extract gold:
-
Mercury plate: the slurry flows through the mercury-plated copper plate, gold and mercury form amalgam and are captured, recovering coarse gold and monomer gold.
-
Amalgamator: The gold amalgam or concentrate scraped from the amalgam plate is further processed to enhance recovery.
-
Sweeping and Tailings Treatment
-
Viscose blanket chute: Used to capture fine-grained and flake gold lost from the amalgamation panels as an important addition to the sweeping process to improve overall recovery.
-
Tailings pond: collects the tailings slurry after the above treatment.
-
Tailings effluent pump: pumps tailings effluent to a designated location for discharge or further treatment.


III. Process program variants
According to the investment budget and the nature of the ore, the core gold mill can be matched with different selection equipment:
-
Gold Mill + Mercury Plate: The most classic and commonly used solution with minimal investment, focusing on the recovery of coarse-grained bare gold.
-
Gold Mill + Shaking Table: Shaking table instead of, or in addition to, mercury plates for concentrating results in higher grade concentrates that are more environmentally friendly and suitable for areas where mercury use is restricted.
-
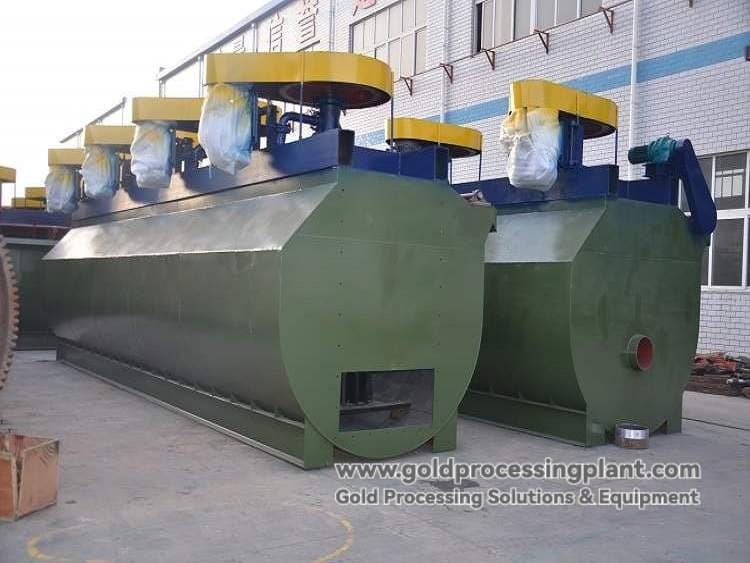
Gold Mill + Flotation Machine: Used to process ores containing fine grained leached gold or associated sulfides, the gold mill serves as the grinding and dissociation equipment, while the flotation machine is responsible for the recovery, which results in a higher recovery rate, but also increased investment and operational complexity.
IV. Program Advantages and Applicable Scenarios



V. Limitations and Considerations

The gold milling process is not a backward-looking process, but rather a cost-effective solution for specific markets and site environments. It is a perfect illustration of the principle of beneficiation that "there is no such thing as the most advanced process, only the most appropriate one".
Before making a selection, it is important to carry out a "gold shaking in a ceramic bowl" test! If you are not sure if your ore is suitable for this process, or if you need a better solution, please contact our technical team for consultation and evaluation.





